![norse-live-attack-map-3[1].png](http://www.cloudmask.com/hs-fs/hubfs/norse-live-attack-map-3%5B1%5D.png?width=826&height=465&name=norse-live-attack-map-3%5B1%5D.png)
This article is the second of a series that explores data breach risks and issues related to regulatory compliance, associated costs and loss of reputation. In “Threats and Consequences” we look at the types of cyber threats and what the consequences might be for businesses that suffer data breaches.
As described in the first article of the series, “What You Need to Know” a data breach occurs when one or more individuals are allowed to read data they are not authorized to access. Once they can read the data, they can steal it and often make changes to it. Depending on the type of data involved, the consequences can include destruction or corruption of databases, the leaking of confidential information, the theft of intellectual property and regulatory requirements to notify and possibly compensate those affected.
According to Bloomberg, data breaches in 2016 increased by 40 percent over 2015. The costs associated with such incidents can be very high and in some cases may threaten the ability of a company to continue in business. As a result, it becomes extremely important for businesses to identify the threats and reduce their exposure.
Data Breach Targets
Business data only becomes a target when it is of value to a third party. Different kinds of data are more or less valuable to third parties and represent different levels of risk to a business. The different types of data include the following:
- Personally Identifiable Information. This includes data such as social security numbers, contact information, birth dates, education and other personal information.
- Financial Information. This includes charge card numbers and expiry dates, bank accounts, investment details and similar data.
- Health Information. This includes details on health conditions, prescription drugs, treatments and medical records.
- Intellectual Property. This includes product drawings and manuals, specifications, scientific formulas, marketing texts and symbols, proprietary software and other material that the business has developed.
- Competition Information. This includes data on competitors, market studies, pricing information and business plans.
- Legal Information. This includes documentation on court cases the company may be pursuing, legal opinions on business practices, merger and acquisition details and regulatory rulings.
- IT Security Data. This includes lists of user names and passwords, encryption keys, security strategies and network structure.
These types of information attract the attention of third parties for whom the data has value. Personal, financial and health information can be sold and used for marketing, fraud and identity theft. Intellectual property can be sold and used to develop products and services similar to those of your business. Competitive information can be sold and used by your competitors to block your plans and leaked legal information may damage your legal position. Data on IT security is a valuable target in itself because it lets the unauthorized parties gain access to all the other types of information on your system.
Data Breach Threats
Threats targeting the different types of data can come from your own employees, from suppliers and consultants who have access to your network and from individuals outside your organization. They can gain access to your data from inside your network, through external email accounts, through mobile devices and through the cloud if your business stores data there. Traditional perimeter protection is no longer enough to keep your data safe from these threats.
Data protection can fail against insiders. Disgruntled employees may decide to leak sensitive information. External individuals can use emails or malicious websites to install malware on employee computers and get user names and passwords that way. Employees of your cloud services supplier often have access to cloud data and email accounts and mobile devices can be lost, hacked or compromised. In the face of such threats, companies have to identify the consequences of corresponding data breaches and find solutions that reduce their risks.
Data Breach Consequences
The consequences for businesses that experience data breaches are severe and increasing. This is mainly due to the increased regulatory burden for notification of the individuals whose data has been compromised. Notification requirements and penalties for businesses suffering a data breach differ with the jurisdiction, both within the United States and Canada and internationally.
Companies that experience a data breach involving customers have to establish where their customers reside and which regulatory authority has jurisdiction. Regulations define the type of data for which notification is required after a breach and they define who has to be notified, how the notification has to be carried out and whether specific authorities have to be notified. Typically breaches involving personal, financial and health data are subject to notification requirements but exact definitions vary for different jurisdictions. Companies doing business internationally may have customers in many jurisdictions and may have to comply with a variety of requirements. The costs of such a process together with legal penalties, possible compensation for damages and any resulting lawsuits can be high enough to constitute an existential threat to some companies.
Data breaches involving the other types of data can severely impact the reputation and business situation of a company. In addition to contractual obligations that may be impacted, the planned sale of a company could be put in question by a data breach, as recently happened with the Yahoo purchase by Verizon. If your competitors become familiar with your business strategies and are able to market products similar to yours at a lower price, your business might not survive.
Solutions to Reduce Risk
While you can keep your perimeter security and other protective measures in place, what you need in addition is a data-centric solution that allows you to tightly control who can read specific files and data sets. Encryption offers this kind of control but it has to be the right kind of encryption. If a specific file or email is encrypted properly, you can control who can read it at all times. Even if there is a data breach of your IT system and unauthorized individuals gain access to the data, they will not be able to read it and a data breach with respect to that data is avoided. Such an application can reduce your data breach risks to acceptable levels and protect your business from ruinously high data breach costs.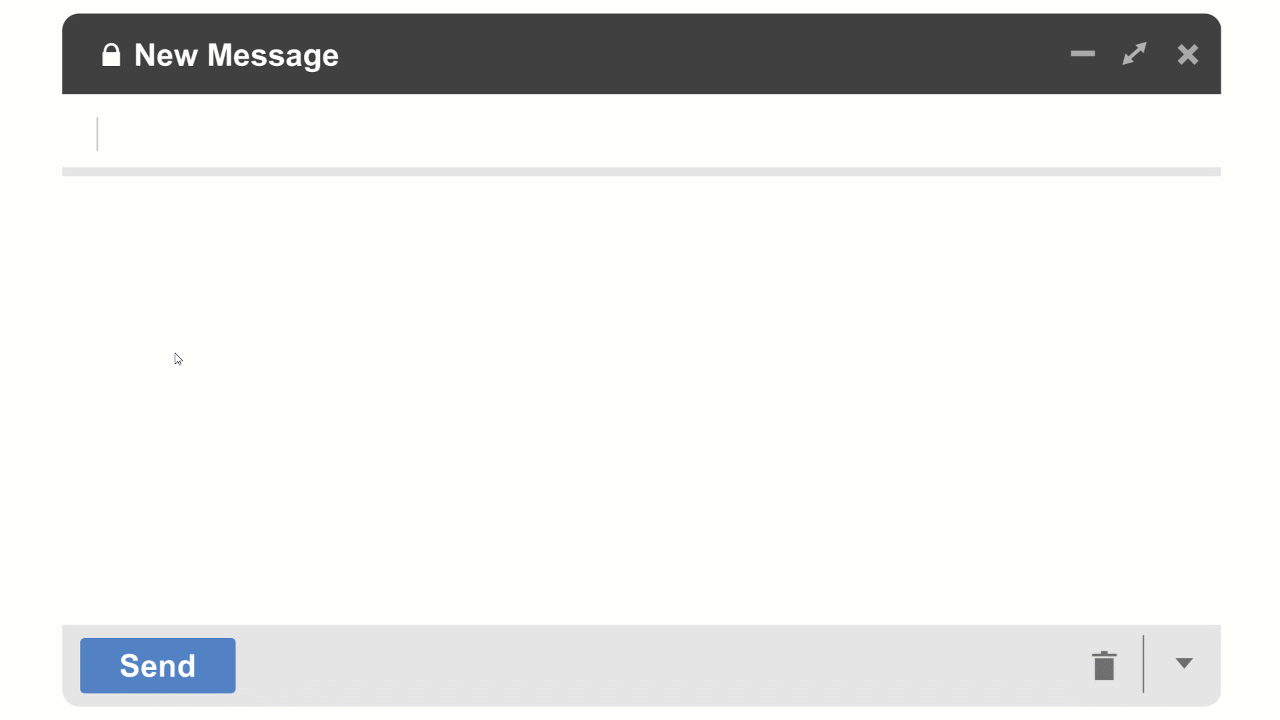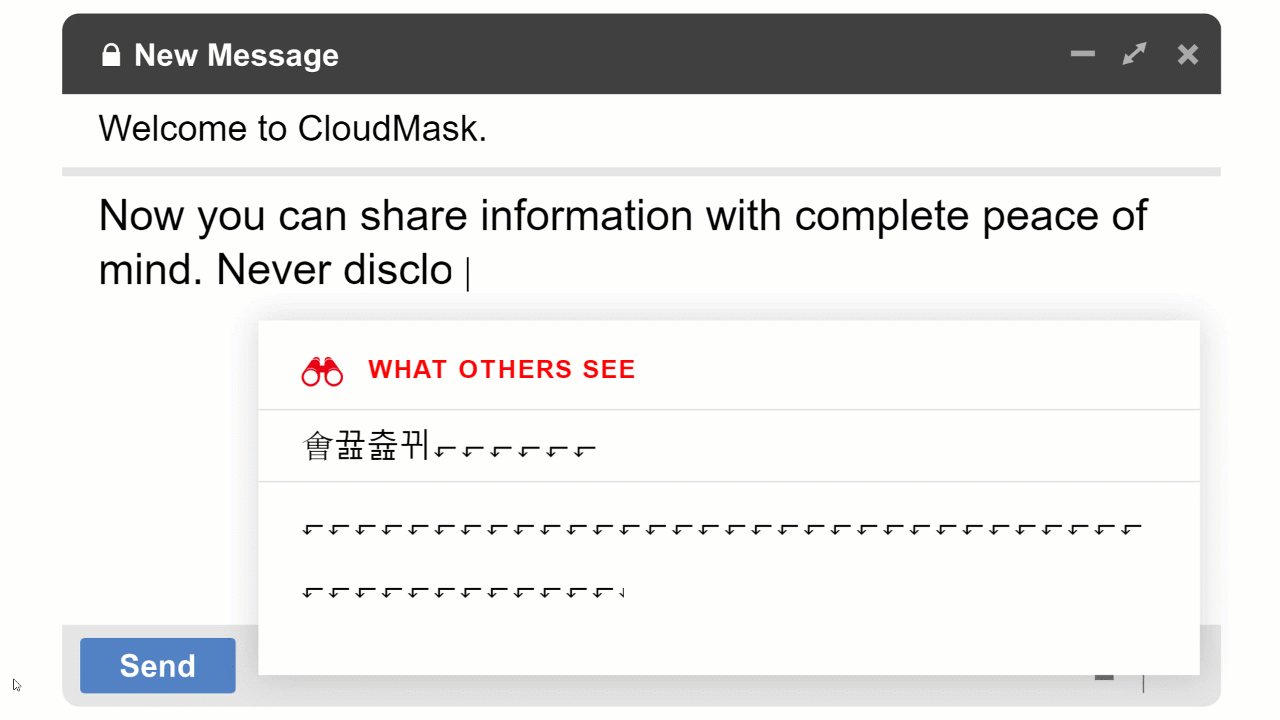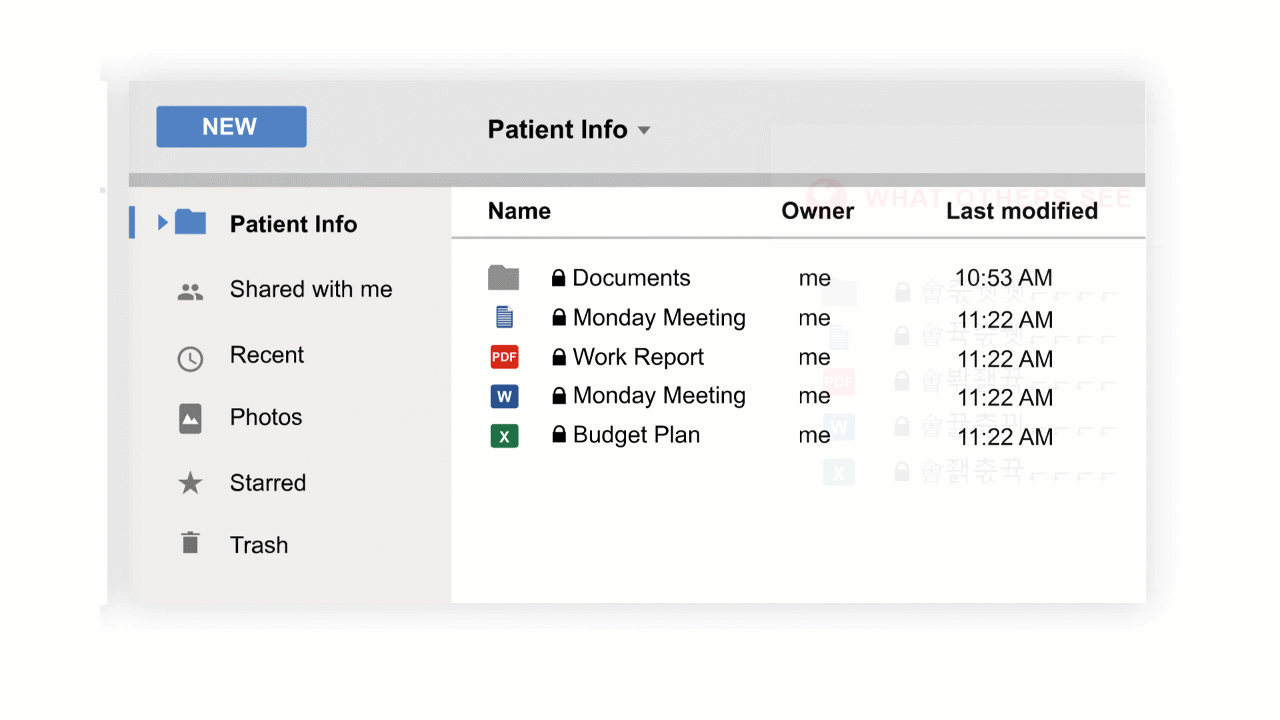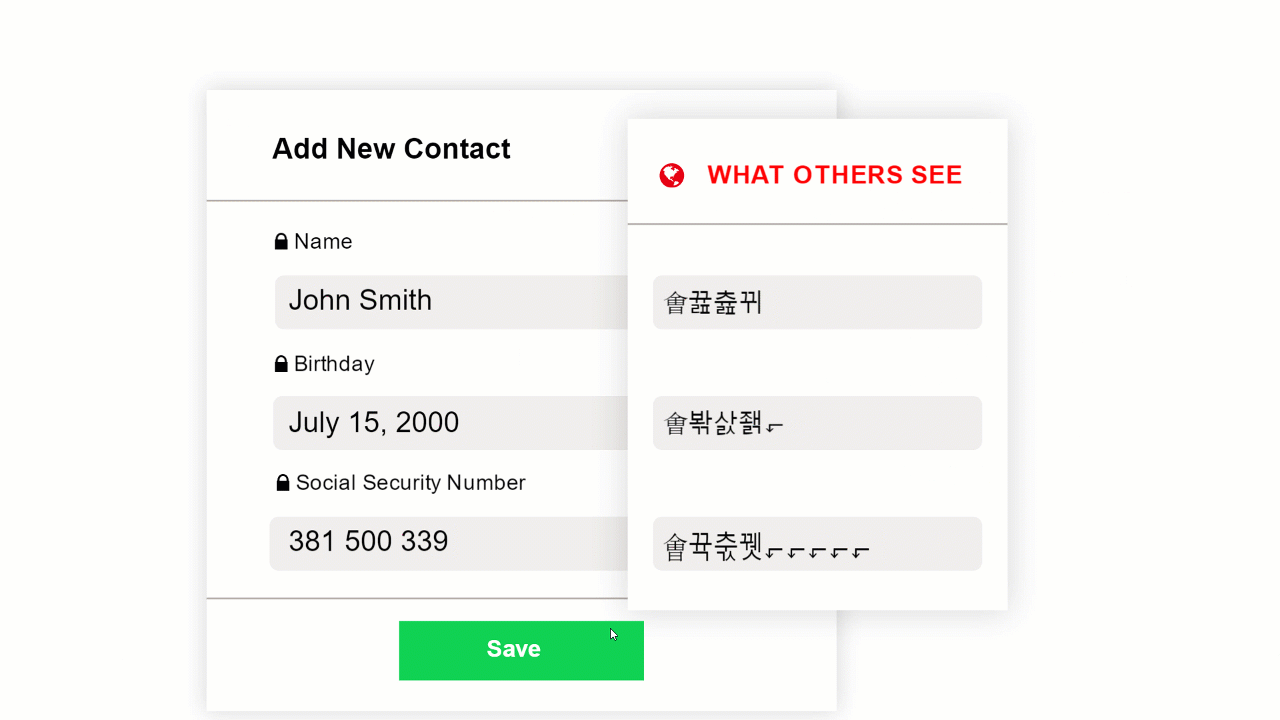
With CloudMask, only your authorized parties can decrypt and see your data. Not hackers with your valid password, Not Cloud Providers, Not Government Agencies, and Not even CloudMask can see your protected data. Twenty-six government cybersecurity agencies around the world back these claims.
Watch our video and demo at www.vimeo.com/cloudmask
Share this article:







